GWP-ASan Internals
本文深入剖析 GWP-ASan 这一概率性内存错误检测工具的原理。
序言
GWP-ASan 是一个概率性内存错误检测工具,是以内存分配器的方式实现的。概率性是指随机保护某些堆分配,在性能和捕获内存错误之间有一个 tradeoff。
Address sanitizer, thread sanitizer 等由编译时插桩和运行时库两部分组成,需要从源码重新编译程序。而 GWP-ASan 则不需要从源码重新编译,因为 GWP-ASan 是以内存分配器的方式实现的。
GWP-ASan 实际上是有多个实现的:
TCMalloc
Chromium
Android
llvm-project
本文 GWP-ASan 原理剖析是基于的 llvm-project 中的 GWP-ASan,llvm-project 版本是 cef07169ec9f46fd25291a3218cf12bef324ea0c
了解 GWP-ASan 原理建议先看下 https://sites.google.com/a/chromium.org/dev/Home/chromium-security/articles/gwp-asan 有一个基本的了解。
原理
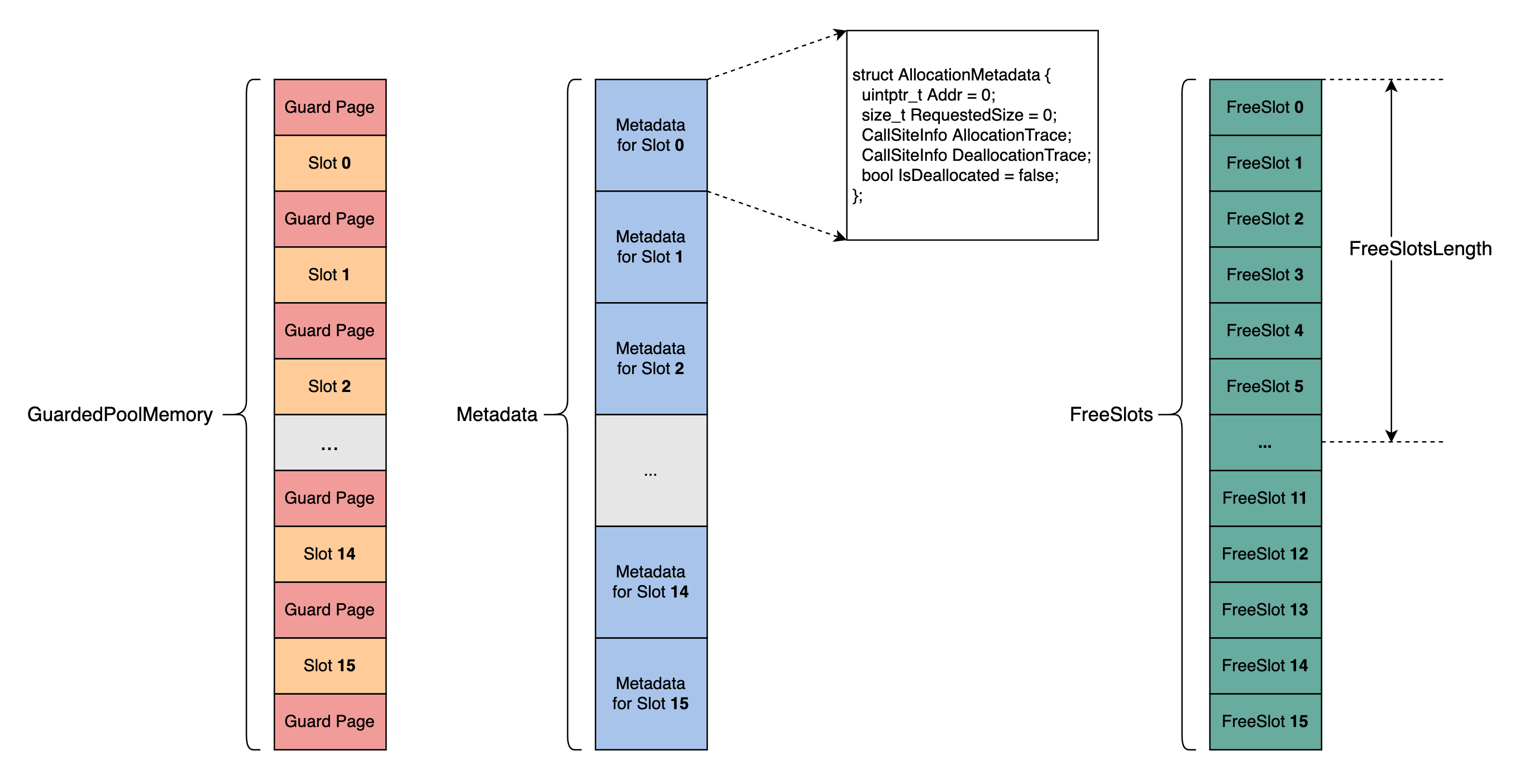
GWP-ASan 的核心数据结构就是上图中的 GuardedPoolMemory, Metadata, FreeSlots。
GuardedPoolMemory
包含 16 个 Slot 和 16+1 个 GuardPage。Slot 和 GuardPage 的大小都是 PageSize。Slot 的数量可以由参数 MaxSimultaneousAllocations (Number of simultaneously-guarded allocations available in the pool. Defaults to 16) 通过环境变量进行设置
每一次由 GWP-ASan 分配出去的内存,都是位于在 GuardedPoolMemory Slot 中的内存
每一次可分配的内存大小,最大为 PageSize
每一个 Slot 用于一次内存分配后,该 Slot 不会再用于另外的内存分配,直至这块 chunk 被释放。假设上一次分配的内存位于 Slot 0 中,并且分配的内存还没有被释放,就算 Slot 0 中还有足够的大小可供这一次分配,这一次分配的内存还是会去其他的 Slot 中分配
Metadata
每一个 GuardedPoolMemory Slot 对应 Metadata 中的一个 AllocationMetadata
Metadata 中记录了 Addr, RequestedSize, AllocationTrace, DeallocationTrace, IsDeallocated 的信息
FreeSlots
FreeSlot 中记录的是之前分配出去的且当前已经被释放了的 GuardedPoolMemory Slot Index。如果 GuardedPoolMemory 中的 16 个 Slot 都已经分配出去过了(注,这 16 个 Slot 当前有可能已经被释放、也有可能没有释放),此时需要再分配内存时,是随机去 FreeSlots 选择一个 FreeSlot 对应的 GuardedPoolMemory Slot 进行分配。如果 FreeSlots 中没有 FreeSlot,则分配失败
FreesSlotsLength 记录的是当前 FreeSlots 的有效长度
检测到内存错误立即 Crash
整个 GuardedPoolMemory 是通过 mmap 申请的,初始时都是 PROT_NONE 权限。只有在将 Slot 的一部分大小分配出去时,才将该 Slot 的权限通过 mprotect 设置为 PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE,等到释放这块内存时,又将 Slot 权限设置为 PROT_NONE
这样一旦有 heap buffer overflow, heap buffer underflow 或者 use after free 这样的错误,就会因为没有权限访问而 crash
检测 heap buffer overflow
例子
#include <cstdlib>
int main() {
char *Ptr = reinterpret_cast<char *>(malloc(4000));
volatile char x = *(Ptr + 4016);
volatile char y = *(Ptr + 4096);
return 0;
}
$ clang++ -fsanitize=scudo heap_buffer_overflow.cpp -o heap_buffer_overflow
$ GWP_ASAN_OPTIONS='SampleRate=1' ./heap_buffer_overflow
注意到上述例子 heap buffer overflow 的例子,有时候能够检测到 *(Ptr + 4016) 这次越界访问,有时候则检测不到 *(Ptr + 4016) 这次越界访问(只检测到了 *(Ptr + 4096) 的越界访问)。多次运行 ./heap_buffer_overflow 会得到两种报告:
Case1, Buffer Overflow at 4096 bytes to the right of a 4000-byte allocation
*** GWP-ASan detected a memory error *** Buffer Overflow at 0x7bfff7a41000 (4096 bytes to the right of a 4000-byte allocation at 0x7bfff7a40000) by thread 235485 here: #0 heap_buffer_overflow(+0x290b9) [0x55555557d0b9] #1 heap_buffer_overflow(+0x293a5) [0x55555557d3a5] #2 heap_buffer_overflow(+0x295e9) [0x55555557d5e9] #3 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libpthread.so.0(+0x12730) [0x7ffff7ca0730] #4 heap_buffer_overflow(main+0x2e) [0x5555555a115e] #5 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(__libc_start_main+0xeb) [0x7ffff7aac09b] #6 heap_buffer_overflow(_start+0x2a) [0x55555555a53a] 0x7bfff7a41000 was allocated by thread 235485 here: #0 heap_buffer_overflow(+0x290c9) [0x55555557d0c9] #1 heap_buffer_overflow(+0x26d25) [0x55555557ad25] #2 heap_buffer_overflow(+0x27edb) [0x55555557bedb] #3 heap_buffer_overflow(+0x41f82) [0x555555595f82] #4 heap_buffer_overflow(main+0x19) [0x5555555a1149] #5 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(__libc_start_main+0xeb) [0x7ffff7aac09b] #6 heap_buffer_overflow(_start+0x2a) [0x55555555a53a] *** End GWP-ASan report ***Case2, Buffer Overflow at 4016 bytes to the right of a 4000-byte allocation
*** GWP-ASan detected a memory error *** Buffer Overflow at 0x7bfff7a41010 (4016 bytes to the right of a 4000-byte allocation at 0x7bfff7a40060) by thread 235483 here: #0 heap_buffer_overflow(+0x290b9) [0x55555557d0b9] #1 heap_buffer_overflow(+0x293a5) [0x55555557d3a5] #2 heap_buffer_overflow(+0x295e9) [0x55555557d5e9] #3 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libpthread.so.0(+0x12730) [0x7ffff7ca0730] #4 heap_buffer_overflow(main+0x21) [0x5555555a1151] #5 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(__libc_start_main+0xeb) [0x7ffff7aac09b] #6 heap_buffer_overflow(_start+0x2a) [0x55555555a53a] 0x7bfff7a41010 was allocated by thread 235483 here: #0 heap_buffer_overflow(+0x290c9) [0x55555557d0c9] #1 heap_buffer_overflow(+0x26d25) [0x55555557ad25] #2 heap_buffer_overflow(+0x27edb) [0x55555557bedb] #3 heap_buffer_overflow(+0x41f82) [0x555555595f82] #4 heap_buffer_overflow(main+0x19) [0x5555555a1149] #5 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(__libc_start_main+0xeb) [0x7ffff7aac09b] #6 heap_buffer_overflow(_start+0x2a) [0x55555555a53a] *** End GWP-ASan report ***
检测原理
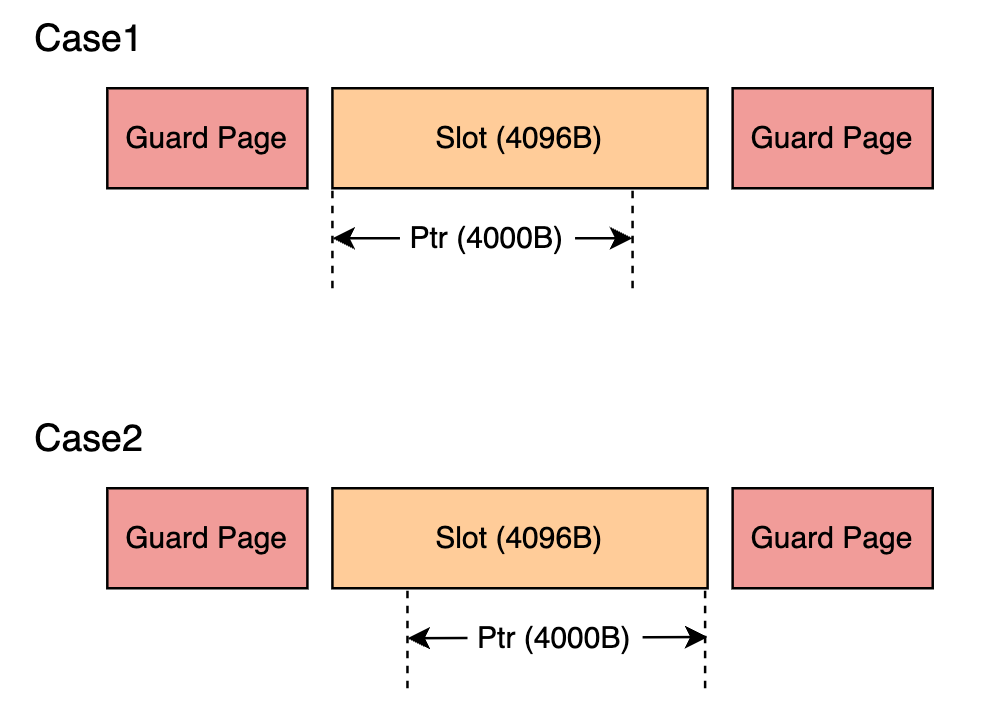
为什么会出现上述现象,原因见下图:
GWP-ASan 是对于每一次 allocate 都是随机选择 left-align or right-align 的
对于 case1 来说,返回给用户的 Ptr 地址就是 Slot 的起始地址,所以当访问
*(Ptr + 4016)时,Ptr + 4016 还是在该 Slot 中,也就是有权限访问的,也就不会 crash,所以检测不到*(Ptr + 4016)此处溢出。对于 case2 来说,返回给用户的 Ptr 地址就是 SlotEnd - Size,所以当访问
*(Ptr + 4016)时,Ptr + 4016 是位于该 GuardPage 中的,没有权限访问,故能检测出*(Ptr + 4016)此处溢出。对于 case1 和 case2 来说,都能检测
*(Ptr + 4096)到这次溢出,这是因为 case1 和 case2 中,Ptr + 4096 都位于 Guard Page 中,因此都能检测到这里的溢出。
检测 use after free
例子
#include <cstdlib>
int main() {
char *Ptr = reinterpret_cast<char *>(malloc(10));
for (unsigned i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
*(Ptr + i) = 0x0;
}
free(Ptr);
volatile char x = *Ptr;
return 0;
}
$ clang++ -fsanitize=scudo use_after_free.cpp -o use_after_free
$ GWP_ASAN_OPTIONS='SampleRate=1' ./use_after_free
*** GWP-ASan detected a memory error ***
Use After Free at 0x7b287e319000 (0 bytes into a 10-byte allocation at 0x7b287e319000) by thread 307939 here:
#0 ./use_after_free(+0x290b9) [0x5603b0fe40b9]
#1 ./use_after_free(+0x293a5) [0x5603b0fe43a5]
#2 ./use_after_free(+0x295e9) [0x5603b0fe45e9]
#3 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libpthread.so.0(+0x12730) [0x7f287e579730]
#4 ./use_after_free(main+0x54) [0x5603b1008184]
#5 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(__libc_start_main+0xeb) [0x7f287e38509b]
#6 ./use_after_free(_start+0x2a) [0x5603b0fc153a]
0x7b287e319000 was deallocated by thread 307939 here:
#0 ./use_after_free(+0x290c9) [0x5603b0fe40c9]
#1 ./use_after_free(+0x26d25) [0x5603b0fe1d25]
#2 ./use_after_free(+0x280eb) [0x5603b0fe30eb]
#3 ./use_after_free(+0x44dc4) [0x5603b0fffdc4]
#4 ./use_after_free(main+0x50) [0x5603b1008180]
#5 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(__libc_start_main+0xeb) [0x7f287e38509b]
#6 ./use_after_free(_start+0x2a) [0x5603b0fc153a]
0x7b287e319000 was allocated by thread 307939 here:
#0 ./use_after_free(+0x290c9) [0x5603b0fe40c9]
#1 ./use_after_free(+0x26d25) [0x5603b0fe1d25]
#2 ./use_after_free(+0x27edb) [0x5603b0fe2edb]
#3 ./use_after_free(+0x41f82) [0x5603b0ffcf82]
#4 ./use_after_free(main+0x19) [0x5603b1008149]
#5 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(__libc_start_main+0xeb) [0x7f287e38509b]
#6 ./use_after_free(_start+0x2a) [0x5603b0fc153a]
*** End GWP-ASan report ***
检测原理
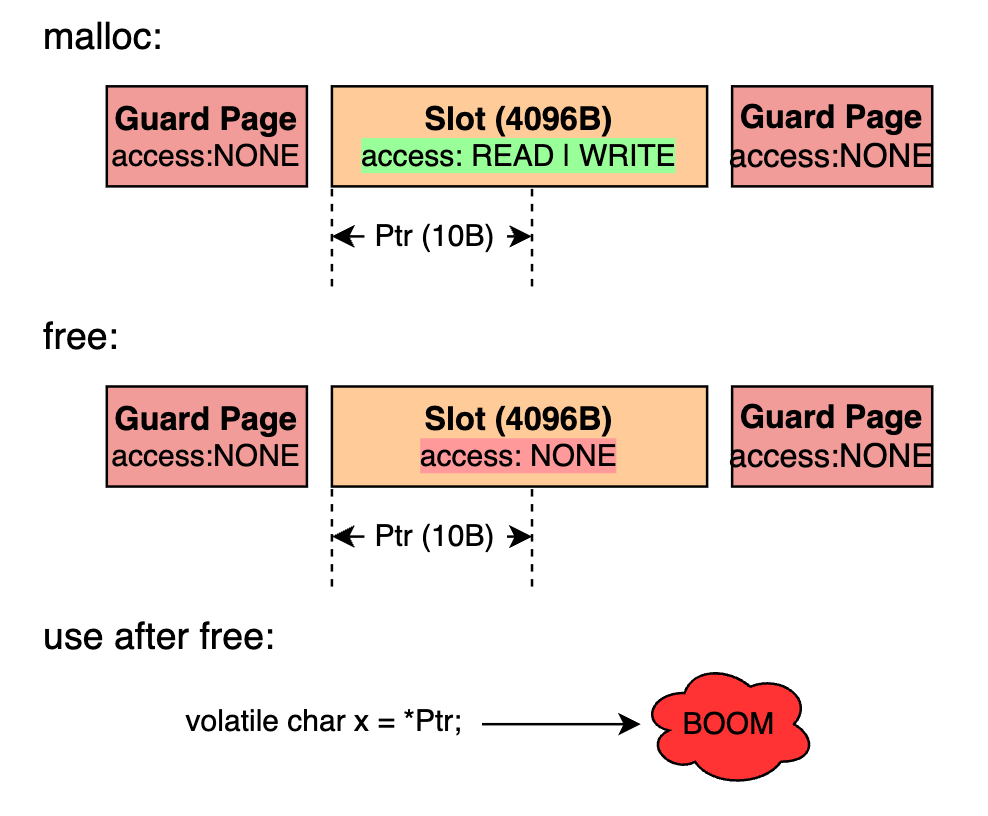
为什么能检测到此处 use after free,原理见下图:
- GWP-ASan 在分配内存时,会将分配出去的 chunk 所在的 Slot 的权限通过 mprotect 设置为 PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE,等到释放这块内存时,又将 Slot 权限设置为 PROT_NONE。这样当访问已经释放的内存时会就是 crash
如果仔细思考下,GWP-ASan 检测 use-after-free 是有局限性的,考虑如下代码:
第 27 行的 use-after-free 就不会被检测出来,因为 underlying slot 又被用于分配了
第 33 行的 use-after-free 虽然会被检测出来,但是 allocation/deallocation stack traces 实际上并不匹配,报告中给出的是 Ptr17 的 allocation/deallocation stack traces
#include <cstdlib>
int main() {
// fill GuardedPoolMemory 16 slots
char *Ptr1 = reinterpret_cast<char *>(malloc(10));
char *Ptr2 = reinterpret_cast<char *>(malloc(10));
char *Ptr3 = reinterpret_cast<char *>(malloc(10));
char *Ptr4 = reinterpret_cast<char *>(malloc(10));
char *Ptr5 = reinterpret_cast<char *>(malloc(10));
char *Ptr6 = reinterpret_cast<char *>(malloc(10));
char *Ptr7 = reinterpret_cast<char *>(malloc(10));
char *Ptr8 = reinterpret_cast<char *>(malloc(10));
char *Ptr9 = reinterpret_cast<char *>(malloc(10));
char *Ptr10 = reinterpret_cast<char *>(malloc(10));
char *Ptr11 = reinterpret_cast<char *>(malloc(10));
char *Ptr12 = reinterpret_cast<char *>(malloc(10));
char *Ptr13 = reinterpret_cast<char *>(malloc(10));
char *Ptr14 = reinterpret_cast<char *>(malloc(10));
char *Ptr15 = reinterpret_cast<char *>(malloc(10));
char *Ptr16 = reinterpret_cast<char *>(malloc(10));
// use and free Ptr1
for (unsigned i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
*(Ptr1 + i) = 0x0;
}
free(Ptr1);
// reuse Ptr1's underlying GuardedPoolMemory slot
char *Ptr17 = reinterpret_cast<char *>(malloc(10));
// use after free, false negative
volatile char x = *Ptr1;
// free Ptr17
free(Ptr17);
// use after free, wrong allocation/deallocation stack traces.
volatile char y = *Ptr1;
return 0;
}
*** GWP-ASan detected a memory error ***
Use After Free at 0x7b7f2fad5ff0 (0 bytes into a 10-byte allocation at 0x7b7f2fad5ff0) by thread 1005136 here:
#0 ./use_after_free_dumb(+0x30c26) [0x55cc332dac26]
#1 ./use_after_free_dumb(+0x31107) [0x55cc332db107]
#2 ./use_after_free_dumb(+0x30e37) [0x55cc332dae37]
#3 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libpthread.so.0(+0x12730) [0x7f7f2fd1a730]
#4 ./use_after_free_dumb(main+0x168) use_after_free_dumb.cpp:33:21 [0x55cc332ef3c8]
#5 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(__libc_start_main+0xeb) [0x7f7f2fb4009b]
#6 ./use_after_free_dumb(_start+0x2a) [0x55cc332c68da]
0x7b7f2fad5ff0 was deallocated by thread 1005136 here:
#0 ./use_after_free_dumb(+0x30c26) [0x55cc332dac26]
#1 ./use_after_free_dumb(+0x2fbb4) [0x55cc332d9bb4]
#2 ./use_after_free_dumb(+0x306d2) [0x55cc332da6d2]
#3 ./use_after_free_dumb(main+0x162) use_after_free_dumb.cpp:31:3 [0x55cc332ef3c2]
#4 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(__libc_start_main+0xeb) [0x7f7f2fb4009b]
#5 ./use_after_free_dumb(_start+0x2a) [0x55cc332c68da]
0x7b7f2fad5ff0 was allocated by thread 1005136 here:
#0 ./use_after_free_dumb(+0x30c26) [0x55cc332dac26]
#1 ./use_after_free_dumb(+0x2fbb4) [0x55cc332d9bb4]
#2 ./use_after_free_dumb(+0x30547) [0x55cc332da547]
#3 ./use_after_free_dumb(+0x3ee02) [0x55cc332e8e02]
#4 ./use_after_free_dumb(+0x3e935) [0x55cc332e8935]
#5 ./use_after_free_dumb(main+0x143) use_after_free_dumb.cpp:27:9 [0x55cc332ef3a3]
#6 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6(__libc_start_main+0xeb) [0x7f7f2fb4009b]
#7 ./use_after_free_dumb(_start+0x2a) [0x55cc332c68da]
*** End GWP-ASan report ***
GWP-ASan 与 ASan 的对比
- ASan 能检测栈、堆、全局变量的内存错误,而 GWP-ASan 只能检测堆上的内存错误,并且 GWP-ASan 的内存错误检测能力是概率性的 (probabilistic)
- ASan 的额外性能开销和内存开销远高于 GWP-ASan,ASan 通常会增加 2-3 倍的性能和内存开销,而 GWP-ASan 的额外开销则基本可以忽略不计。这是这样 GWP-ASan 可以在生产环境/版本中使用,比如 GWP-ASan 在 Chrome 浏览器中发现了很多内存错误
- GWP-ASan 发现的错误中大约有 90% 都是 use-after-frees,剩下的则是 out-of-bounds reads and writes
总结
实际上 GWP-ASan 的原理非常简单,很早以前就在 ElectricFence or PageHeap 中就有所应用。而这种通过概率采样的方式去处理问题的思路还是非常有意思的,虽然采样的方式会牺牲一定的准确性与能力,但是另一方面就可以在基本不影响应用的环境下去发现问题。不止是 GWP-ASan,AutoFDO 也是通过随机采样而不是程序插桩的方式,在不影响原本程序性能的情况下,收集程序运行时信息指导反馈编译时优化。