Learn Relocation by Debugging a HWASAN Linker Error
笔者在 Linux/AArch64 环境下使用 HWASAN 时,遇到一 “relocation R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 out of range” 链接错误,在分析解决该链接错误过程中对 linker relocation 以及 HWASAN 都有了更深的理解,因此将分析解决该链接错误的过程梳理总结形成此文。
引言
考虑如下例子:
main.c
// cat main.c extern int foo; extern int bar; int main() { return foo + bar; }global.c
// cat global.c int foo; int bar;编译链接 & 链接报错
$ clang -fno-PIC -fsanitize=hwaddress -c global.c -o global.o $ clang -fno-PIC -c main.c -o main.o $ clang -fuse-ld=lld -fsanitize=hwaddress main.o global.o -o a.out ld.lld: error: main.o:(function main: .text+0x8): relocation R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 out of range: 3242591731706900480 is not in [-4294967296, 4294967295]; references 'foo'
注意:在编译 global.c 时添加了参数 -fsanitize=hwaddress,在编译 main.c 时没有添加参数 -fsanitize=hwaddress,在链接时两个编译单元生成可执行文件 a.out 时也添加了参数 -fsanitize=hwaddress。即目标文件 global.o 是被 HWASAN 插桩的,而目标文件 main.o 是没有被 HWASAN 插桩的,在链接 global.o 和 main.o 生成可执行文件 a.out 时,链接命令中的参数 -fsanitize=hwaddress 使得可执行文件 a.out 链接了 HWASAN runtime: libclang_rt.hwasan.a。
为什么编译 global.c 时添加参数 -fsanitize=hwaddress,而编译 main.c 时却没有添加参数 -fsanitize=hwaddress?
在实际开发中,一个项目通常有很多依赖库:有些依赖库是以源码形式依赖的,而有些依赖库则是以预编译好的 .a 或者 .so 的形式依赖的。所以这样的项目在使用 HWASAN 时,HWASAN 只能对那些从源码编译的部分进行插桩,对于预编译依赖库 HWASAN 则无法插桩。上述例子中在编译 main.c 时没有添加参数 -fsanitize=hwaddress 正是为了模拟预编译 .a 依赖库没有被 HWASAN 插桩这一情况。
实际上,上述例子正是为了分析实际项目中使用 HWASAN 时遇到的 “relocation R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 out of range” 这一链接错误而抽象出来的一个最小复现示例。
Relocation
在分析使用 HWASAN 时遇到的这个 “relocation R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 out of range” 链接错误之前,需要先了解重定位。
还是通过同一个例子来学习重定位,但暂时先抛开 HWASAN:
$ clang -fno-PIC -c global.c -o global.o
$ clang -fno-PIC -c main.c -o main.o
$ clang -fuse-ld=lld main.o global.o -o a.out
首先通过 objdump -d a.out | awk -v RS= '/^[[:xdigit:]]+ <main>/' 查看 a.out 中 main 函数的汇编代码:
00000000000107f4 <main>:
107f4: d10043ff sub sp, sp, #0x10
107f8: b9000fff str wzr, [sp, #0xc]
107fc: 90000108 adrp x8, 0x30000
10800: b94b5508 ldr w8, [x8, #0xb54]
10804: 90000109 adrp x9, 0x30000
10808: b94b5929 ldr w9, [x9, #0xb58]
1080c: 0b090100 add w0, w8, w9
10810: 910043ff add sp, sp, #0x10
10814: d65f03c0 ret
adrp x8, 0x30000 + ldr w8, [x8, #0xb54] 是从地址 0x30b54 读取 4 字节的内容保存在 x8 寄存器中,adrp x9, 0x30000 + ldr w9, [x9, #0xb58] 是从地址 0x30b58 读取 4 字节的内容保存在 x9 寄存器中,add w0, w8, w9 是将保存在 x8 和 x9 寄存器的值相加将结果存储到 w0 寄存器中。这一系列指令对应的是源代码中的 return foo + bar; 这条语句,也就是说全局变量 foo 的地址是 0x30b54,全局变量 bar 的地址是 0x30b58。
如何验证:全局变量 foo 的地址是 0x30b54,全局变量 bar 的地址是 0x30b58?
通过 nm 命令(或 readelf)可以确认 a.out 中全局变量 foo 和 bar 的地址分别是 0x30b54 和 0x30b58:
$ nm a.out | grep -E 'foo|bar'
0000000000030b58 B bar
0000000000030b54 B foo
现在考虑这样一个问题:a.out 是 main.o 和 global.o 的链接产物,a.out 中全局变量 foo 和 bar 的地址是 0x30b54 和 0x30b58。编译单元 main.c 中引用了全局变量 foo 和 bar,而这两个全局变量是在编译单元 global.c 中定义的,编译 main.c 生成目标文件 main.o 时显然是不知道全局变量 foo 和 bar 的地址的,那么在最终链接产物 a.out 中是如何让 main 函数可以寻址到全局变量 foo 和 bar 的?
通过 objdump -d main.o | awk -v RS= '/^[[:xdigit:]]+ <main>/' 查看 main.o 中 main 函数的汇编代码,可以看到 main.o 中获取全局变量 foo 的值的指令是 adrp x8, 0 + ldr w8, [x8]。对比 a.out 中获取全局变量 foo 的值的指令是 adrp x8, 0x30000 + ldr w8, [x8, #0xb54],即 main.o 中 adrp x8, 0 + ldr w8, [x8] 指令并没有填真正的全局变量 foo 的地址,而是用 0 作为占位符填到指令中。
0000000000000000 <main>:
0: d10043ff sub sp, sp, #0x10
4: b9000fff str wzr, [sp, #12]
8: 90000008 adrp x8, 0
c: b9400108 ldr w8, [x8]
10: 90000009 adrp x9, 0
14: b9400129 ldr w9, [x9]
18: 0b090100 add w0, w8, w9
1c: 910043ff add sp, sp, #0x10
20: d65f03c0 ret
main.o 中是不知道全局变量 foo 和 bar 地址的,a.out 是知道全局变量 foo 和 bar 地址的,所以其实可以猜到是链接器在链接时将引用全局变量 foo 的指令 adrp x8, 0 + ldr w8, [x8] 修改为 adrp x8, 0x30000 + ldr w8, [x8, #0xb54],填入了全局变量 foo 的地址。这其实就是重定位 (relocation),重定位就是在链接器确定每个符号定义的地址后,修改所有对这些符号的引用,使之指向这些符号定义的地址。
那么链接器是怎么知道哪些位置需要重定位的?答案是依赖于保存在目标文件中的重定位信息。
可以通过 readelf -rW 查看重定位信息。
$ readelf -rW main.o
Relocation section '.rela.text' at offset 0x1d8 contains 4 entries:
Offset Info Type Symbol's Value Symbol's Name + Addend
0000000000000008 0000000700000113 R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 0000000000000000 foo + 0
000000000000000c 000000070000011d R_AARCH64_LDST32_ABS_LO12_NC 0000000000000000 foo + 0
0000000000000010 0000000800000113 R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 0000000000000000 bar + 0
0000000000000014 000000080000011d R_AARCH64_LDST32_ABS_LO12_NC 0000000000000000 bar + 0
根据上述重定位信息可知:
在 main.o 的 text section 偏移为 0x8 处和 0xc 处引用了符号 foo,重定位类型分别为 R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 和 R_AARCH64_LDST32_ABS_LO12_NC
在 main.o 的 text section 偏移为 0x10 处和 0x14 处引用了符号 bar,重定位类型分别为 R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 和 R_AARCH64_LDST32_ABS_LO12_NC
注:
Offset:需要修改的符号引用的位置。在本例中表示需要修改的符号引用的位置相对 text section 起始位置的偏移量(字节)。Type:重定位类型。用于指示链接器如何修改该符号引用的值。Info:低 4 字节表示重定位类型,高 4 字节表示表示符号表索引。符号表索引表示需要修改的符号引用在.symtabsection 中的索引。重定位类型 R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 对应编号就是 0x113=275,重定位类型 R_AARCH64_LDST32_ABS_LO12_NC 对应编号就是 0x11d=285
Symbol's Value和Symbol's Name就是对应的.symtabsection 条目中Value和Name的值。$ readelf -sW main.o Symbol table '.symtab' contains 9 entries: Num: Value Size Type Bind Vis Ndx Name 7: 0000000000000000 0 NOTYPE GLOBAL DEFAULT UND foo 8: 0000000000000000 0 NOTYPE GLOBAL DEFAULT UND barAddend:有符号常数,一些重定位类型要使用它对被修改符号引用的值做偏移调整。
下面详解链接器将引用全局变量 foo 的指令 adrp x8, 0 + ldr w8, [x8] 修改为 adrp x8, 0x30000 + ldr w8, [x8, #0xb54] 的重定位过程:
根据 https://github.com/ARM-software/abi-aa/blob/main/aaelf64/aaelf64.rst#relocation 可以找到重定位类型 R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 和 R_AARCH64_LDST32_ABS_LO12_NC 的重定位计算公式:
| Code | Name | Operation | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 275 | R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 | Page(S+A)-Page(P) | Set an ADRP immediate value to bits [32:12] of the X; check that -2^32 <= X < 2^32 |
| 285 | R_AARCH64_LDST32_ABS_LO12_NC | S + A | Set the LD/ST immediate value to bits [11:2] of X. No overflow check |
注:
S(when used on its own) is the address of the symbol.Ais the addend for the relocationPis the address of the place being relocated (derived fromr_offset).Xis the result of a relocation operation, before any masking or bit-selection operation is appliedPage(expr)is the page address of the expression expr, defined as (expr & ~0xFFF). (This applies even if the machine page size supported by the platform has a different value.)
将
adrp x8, 0修改为adrp x8, 0x30000的重定位过程重定位信息
Relocation section '.rela.text' at offset 0x1d8 contains 4 entries: Offset Info Type Symbol's Value Symbol's Name + Addend 0000000000000008 0000000700000113 R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 0000000000000000 foo + 0readelf -sW a.out找到符号 foo 最终所在的地址是 0x30b54,即S= 0x30b54根据重定位信息可知 addend 为 0 即
A= 0objdump -d a.out找到adrp x8, 0指令最终在 a.out 中的地址为 0x107f4 + 0x8,即P= 0x107fcX= Page(S+A)-Page(P) = Page(0x30b54 + 0) - Page(0x107fc) = (0x30b54 & ~0xFFF) - (0x107fc & ~0xFFF) = 0x20000R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 类型的重定位操作是 “Set an ADRP immediate value to bits [32:12] of the X; check that -2^32 <= X < 2^32”
显然 -2^32 <= 0x20000 < 2^32,所以接下来就是将
adrp x8, 0指令的 immediate value 设置为 0x20000 的 [32:12] bits。ADRP指令编码如下,[30:29] bits 是 immediate value low bits, [23:5] for immediate value high bits。
重定位之前
adrp x8, 0指令的编码为 0x90000008 即1001 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1000,将adrp x8, 0指令的 immediate value 设置为 0x20000 的 [32:12] bits 即 0b100000,就是将adrp x8, 0指令的 immediate value low bits 设置为 0b00,将adrp x8, 0指令的 immediate value high bits 为 0b1000,所以重定位之后后指令编码变为1001 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 0000 1000即 0x90000108。对指令 0x90000108 进行解码:
107fc: 90000108 adrp x8, 0x30000:当前 PC 值为 0x107fc,PC with its bottom 12 bits cleared 为 0x10000,immediate value 即 0b100000 左移 12 位为 0x20000,然后 0x10000 + 0x20000 = 0x30000,destination register 为 0b1000 即 x8 寄存器,所以该指令表示将 0x30000 保存在 x8 寄存器中。
将
ldr w8, [x8]修改为ldr w8, [x8, #0xb54]的重定位过程重定位信息
Offset Info Type Symbol's Value Symbol's Name + Addend 000000000000000c 000000070000011d R_AARCH64_LDST32_ABS_LO12_NC 0000000000000000 foo + 0readelf -sW a.out找到符号 foo 最终所在的地址是 0x30b54,即S= 0x30b54根据重定位信息可知 addend 为 0 即
A= 0X= S+A = 0x30b54 + 0 = 0x30b54R_AARCH64_LDST32_ABS_LO12_NC 类型的重定位操作是 “Set the LD/ST immediate value to bits [11:2] of X. No overflow check”
X= 0x30b54 的 [11:2] bits 为 0b1011010101。ldr w9, [x8]指令的编码为 0xb9400108 即1011 1001 0100 0000 0000 0001 0000 1000,[21:10] bits 为 immediate value。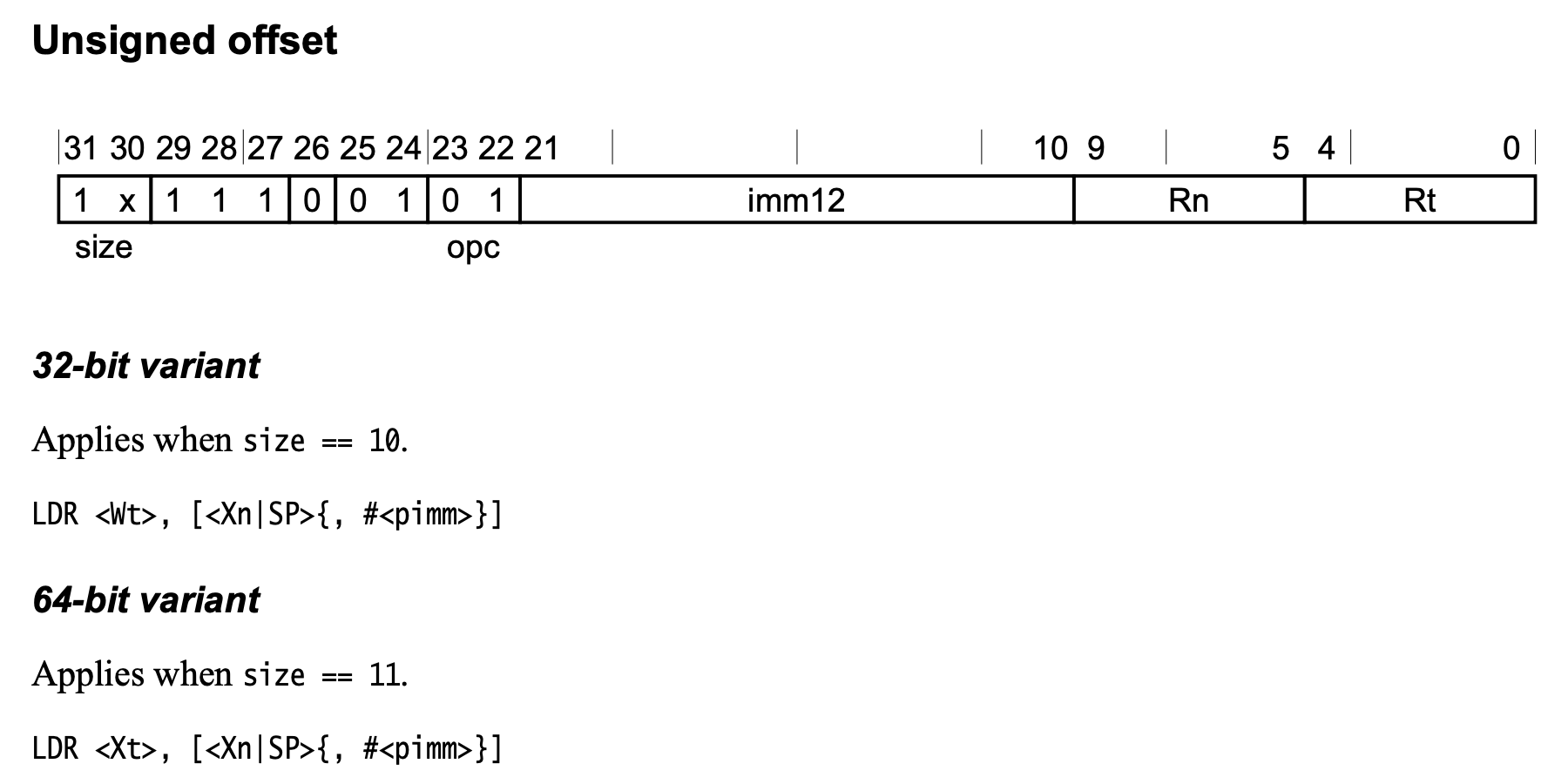
注:
<Wt>: Is the 32-bit name of the general-purpose register to be transferred, encoded in the “Rt” field.<Xt>: Is the 64-bit name of the general-purpose register to be transferred, encoded in the “Rt” field.<Xn|SP>: Is the 64-bit name of the general-purpose base register or stack pointer, encoded in the “Rn” field.<pimm>: For the 32-bit variant: is the optional positive immediate byte offset, a multiple of 4 in the range 0 to 16380, defaulting to 0 and encoded in the “imm12” field as /4. For the 64-bit variant: is the optional positive immediate byte offset, a multiple of 8 in the range 0 to 32760, defaulting to 0 and encoded in the “imm12” field as /8
重定位之前指令的编码为 0xb9400108 即
1011 1001 0100 0000 0000 0001 0000 1000,将指令的 immediate value 设置为 0b1011010101 得到重定位之后指令的编码为1011 1001 0100 1011 0101 0101 0000 1000即 0xb94b5508。对指令 0xb94b5508 进行解码:
ldr w9, [x8, #0xb54]:size = 0b10,Rt = 0b01000 = 8,Rn = 0b01000 = 8,imm12 = 0b1011010101,<Wt>= w8 寄存器,<Xn|SP>= x8 寄存器,#<pimm> = 0b1011010101 * 4 = 0xb54,因此该指令表示从内存地址 x8 + 0xb54 处读取 4 字节内容保存在 w8 寄存器中。
HWASAN relocation overflow
了解重定位后,就可以对本文最开始提到的 “relocation R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 out of range” 链接错误进行分析了:
$ clang -fno-PIC -fsanitize=hwaddress -c global.c -o global.hwasan.o
$ clang -fno-PIC -c main.c -o main.o
$ clang -fuse-ld=lld -fsanitize=hwaddress main.o global.hwasan.o -o a.out
ld.lld: error: main.o:(function main: .text+0x8): relocation R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 out of range: 3242591731706900480 is not in [-4294967296, 4294967295]; references 'foo'
为了方便分析,可以通过链接器提供的 -noinhibit-exec 选项,使得尽管出现 “relocation R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 out of range” 链接错误仍然能够生成链接产物 a.out。
$ clang -Wl,-noinhibit-exec -fuse-ld=lld -fsanitize=hwaddress main.o global.hwasan.o -o a.out
$ readelf -sW a.out | grep -E "foo|bar"
2442: 2d0000000009bae0 4 OBJECT GLOBAL DEFAULT 26 foo
2443: 2e0000000009baf0 4 OBJECT GLOBAL DEFAULT 26 bar
通过 readelf -rW 查看重定位信息,由重定位信息可知:在 main.o 的 text section 偏移为 0x8 处引用了符号 foo,重定位类型分别为 R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21。
$ readelf -rW main.o
Relocation section '.rela.text' at offset 0x1d8 contains 4 entries:
Offset Info Type Symbol's Value Symbol's Name + Addend
0000000000000008 0000000700000113 R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 0000000000000000 foo + 0
000000000000000c 000000070000011d R_AARCH64_LDST32_ABS_LO12_NC 0000000000000000 foo + 0
0000000000000010 0000000800000113 R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 0000000000000000 bar + 0
0000000000000014 000000080000011d R_AARCH64_LDST32_ABS_LO12_NC 0000000000000000 bar + 0
根据上一节 “Relocation” 的内容,R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 的重定位计算方式为 Page(S+A)-Page(P)。
S即 符号 foo 的地址。通过readelf -sW a.out找到符号 foo 的地址是 0x2d0000000009bae0,即S= 0x2d0000000009bae0A即 addend。根据重定位信息可知 addend 为 0 即A= 0P即 需要进行重定位的位置。objdump -d a.out找到adrp x8, 0指令最终在 a.out 中的地址为 0x780d8 + 0x8,即P= 0x780e0计算
X= Page(S+A)-Page(P) = Page(0x2d0000000009bae0 + 0) - Page(0x780e0) = (0x2d0000000009bae0 & ~0xFFF) - (0x780e0 & ~0xFFF) = 3242591731706900480R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 类型的重定位操作是 “Set an ADRP immediate value to bits [32:12] of the X; check that -2^32 <= X < 2^32”,显然 3242591731706900480 不在 [-2^32, 2^32) 区间内,所以链接器报错 “relocation R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 out of range”
所以接下来问题就是为什么编译 global.c 时开启 HWASAN 后使得符号 foo 的地址变为了 3242591731706900480 这么大的值。
查看 global.hwasan.o 对应的汇编代码,可以看到 HWASAN 为 global.c 额外生成了 4 个 STT_OBJECT 符号 .Lfoo.hwasan 和 .Lfoo.hwasan.descriptor,.Lbar.hwasan 和 .Lbar.hwasan.descriptor:
$ clang -fno-PIC -fsanitize=hwaddress -S global.c -o -
.type .Lfoo.hwasan,@object // @foo.hwasan
.data
.p2align 4, 0x0
.Lfoo.hwasan:
.word 0 // 0x0
.ascii "\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\000-"
.size .Lfoo.hwasan, 16
.type .Lfoo.hwasan.descriptor,@object // @foo.hwasan.descriptor
.section hwasan_globals,"ao",@progbits,.Lfoo.hwasan,unique,2
.p2align 3, 0x0
.Lfoo.hwasan.descriptor:
.word .Lfoo.hwasan-.Lfoo.hwasan.descriptor
.word 754974724 // 0x2d000004
.size .Lfoo.hwasan.descriptor, 8
.type .Lbar.hwasan,@object // @bar.hwasan
.data
.p2align 4, 0x0
.Lbar.hwasan:
.word 0 // 0x0
.ascii "\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\000."
.size .Lbar.hwasan, 16
.type .Lbar.hwasan.descriptor,@object // @bar.hwasan.descriptor
.section hwasan_globals,"ao",@progbits,.Lbar.hwasan,unique,3
.p2align 3, 0x0
.Lbar.hwasan.descriptor:
.word .Lbar.hwasan-.Lbar.hwasan.descriptor
.word 771751940 // 0x2e000004
.size .Lbar.hwasan.descriptor, 8
.globl foo
.set foo, .Lfoo.hwasan+3242591731706757120
.size foo, 4
.globl bar
.set bar, .Lbar.hwasan+3314649325744685056
.size bar, 4
.Lfoo.hwasan的大小为 16-bytes,为 16-bytes 对齐,前 15-bytes 被初始化为 0x0,最后一个 byte 被初始化为 0x2d。.Lfoo.hwasan.descriptor顾名思义就是用于描述.Lfoo.hwasan的,保存在最终链接二进制的 hwasan_globals section 中,.Lfoo.hwasan.descriptor依次保存了以下内容:.Lfoo.hwasan相对于自己的偏移(占 4-bytes)、.Lfoo.hwasan对应的全局变量 foo 的 size and tag(共占 4-bytes,tag 保存在 top-byte,size 保存在低 3-bytes),全局变量 foo 的 size 为 4-bytes,tag 为 0x2d。.Lbar.hwasan的大小为 16-bytes,为 16-bytes 对齐,前 15-bytes 被初始化为 0x0,最后一个 byte 被初始化为 0x2e。.Lbar.hwasan.descriptor依次保存了以下内容:.Lbar.hwasan相对于自己的偏移(占 4-bytes)、.Lbar.hwasan对应的全局变量 bar 的 size and tag(共占 4-bytes,tag 保存在 top-byte,size 保存在低 3-bytes),全局变量 bar 的 size 为 4-bytes,tag 为 0x2e。需要注意,开启 HWASAN 后定义全局变量 fo o 是通过 .set assembler directive 将全局变量 foo 的地址设置为
.Lfoo.hwasan的地址 + 0x2d00000000000000,定义全局变量 bar 是通过 .set assembler directive 将全局变量 bar 的地址设置为.Lbar.hwasan的地址 + 0x2e00000000000000
正是因为全局变量 foo 的地址被设置为 .Lfoo.hwasan 的地址 + 0x2d00000000000000,所以在最终的链接产物中符号 foo 的地址才变为了 3242591731706900480=0x2d00000000023000 这么大的值,导致出现 “relocation R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 out of range” 这一链接错误。
那么为什么开启 HWASAN 后会创建 STT_OBJECT 符号 .Lfoo.hwasan,然后通过 .set foo, .Lfoo.hwasan+3242591731706757120 这种方式来设置全局变量 foo 的地址?
这涉及到 HWASAN 的原理,AArch64 的 TBI 特性使得软件可以在 64-bit 虚拟地址的最高字节中存储任意数据,HWASAN 正是基于 TBI 这一特性设计并实现的内存错误检测工具(关于 HWASAN 原理可以阅读我之前写过一篇文章 HWASAN Internals - Enna1’s website)
HWASAN 为了检测全局变量相关的内存错误,会为全局变量生成一个随机 tag 保存在全局变量地址的最高字节。全局变量的随机 tag 是基于其所在的编译单元文件路径计算得到的,在编译时插桩阶段,对于编译单元内的第一个全局变量,其 tag 是对当前编译单元文件路径计算 MD5 哈希值然后取第一个字节得到的,对于编译单元内的后续全局变量,其 tag 则是基于之前全局变量的 tag 递增得到的。
本例中,全局变量 foo 所在的编译单元就是 global.c,MD5 (“global.c”) = 2d5bdd4d2c44c739a456d749bb3e94a0,所以全局变量 foo 的 tag 就是 0x2d,
.set foo, .Lfoo.hwasan+3242591731706757120中的 3242591731706757120 就是由0x2d<<56计算而来,全局变量 bar 的 tag 就是 0x2d+1=0x2e,.set foo, .Lfoo.hwasan+3314649325744685056中的 3314649325744685056 就是由0x2e<<56计算而来。$ echo -n global.c | md5sum 2d5bdd4d2c44c739a456d749bb3e94a0 - $ echo $((0x2d<<56)) 3242591731706757120 $ echo $((0x2e<<56)) 3314649325744685056HWASAN 除了将生成的随机 tag 保存在全局变量地址的最高字节,还会将随机 tag 保存在全局变量对应的 shadow memory 中。
HWASAN 会将每 16-bytes 的 application memory 对应 1-byte 的 shadow memory,所以如果全局变量的大小不是 16-bytes 对齐的,那么会为全局变量添加 padding 使其对齐到 16-bytes。这就是为什么全局变量 foo 的大小是 4-bytes 而
.Lfoo.hwasan的大小则是 16-bytes 且对齐也是 16-bytes。保存在 “hwasan_globals” section 中的
.Lfoo.hwasan.descriptor就是用于设置全局变量 foo 对应的 shadow memory 的。在程序启动时 HWASAN runtime 会遍历 “hwasan_globals” section 中所有的 descriptor,根据 descriptor 中保存的全局变量的大小以及 tag 等信息来设置每个全局变量对应的 shadow memory tag。
总结
至此本文中引言中提到的 “relocation R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 out of range” 这一链接错误的根本原因就清晰了:因 main.c 在编译时是没有开启 HWASAN,而 global.c 在编译时是开启 HWASAN 的,所以定义在 global.c 中的全局变量/符号的地址的 top byte 是被 HWASAN 添加了 tag 的。在 main.c 编译生成的目标文件 main.o 中是通过指令组合 adrp + ldr 来访问全局变量的,且 adrp 处对应的 relocation type 为 R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21。对 R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 该重定位类型链接器在重定位时会检查 X = Page(S+A)-Page(P) 的值是否在 [-2^32, 2^32) 区间内,由于全局变量/符号的地址的 top byte 被 HWASAN 添加了 tag,所以 X = Page(S+A)-Page(P) 一定溢出了 [-2^32, 2^32) 区间,所以链接器在重定位时出现了上述 “relocation R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 out of range” 的报错。
最后介绍下解决本文例子 “relocation R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21 out of range” 链接错误的几种方案:
编译 main.c 和 global.c 时都开启 HWASAN,最简单直接
$ clang -fno-PIC -fsanitize=hwaddress -c global.c -o global.hwasan.o $ clang -fno-PIC -fsanitize=hwaddress -c main.c -o main.hwasan.o $ clang -fuse-ld=lld -fsanitize=hwaddress main.hwasan.o global.hwasan.o -o a.out这是因为编译 main.c 开启 HWASAN 会生成特别的汇编指令,在 main 函数中会通过
adrp+movk+add的指令组合来获取全局变量 foo 的地址,并且这三条指令对应的重定位类型分别为 R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21_NC, R_AARCH64_MOVW_PREL_G3 和 R_AARCH64_ADD_ABS_LO12_NC$ objdump -d main.hwasan.o | awk -v RS= '/^[[:xdigit:]]+ <main>/' ... 38: 90000000 adrp x0, 0 <foo> 3c: f2e00000 movk x0, #0x0, lsl #48 40: 91000000 add x0, x0, #0x0 ... $ readelf -rW main.hwasan.o Offset Info Type Symbol's Value Symbol's Name + Addend 0000000000000038 0000001200000114 R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21_NC 0000000000000000 foo + 0 000000000000003c 0000001200000125 R_AARCH64_MOVW_PREL_G3 0000000000000000 foo + 100000000 0000000000000040 0000001200000115 R_AARCH64_ADD_ABS_LO12_NC 0000000000000000 foo + 0编译 main.c 不开启 HWASAN,编译 global.c 时开启 HWASAN,但是编译 main.c 时开启 PIC
$ clang -fno-PIC -fsanitize=hwaddress -c global.c -o global.hwasan.o $ clang -fPIC -c main.c -o main.pic.o $ clang -fuse-ld=lld -fsanitize=hwaddress main.pic.o global.hwasan.o -o a.out这是因为编译 main.c 开启 PIC 后,main 函数访问全局变量 foo/bar 就是通过 GOT 来间接访问的,所以重定位类型会变为 R_AARCH64_ADR_GOT_PAGE 和 R_AARCH64_LD64_GOT_LO12_NC,也就不会出现 relocation overflow:
0000000000000038 0000001200000137 R_AARCH64_ADR_GOT_PAGE 0000000000000000 foo + 0 000000000000003c 0000001200000138 R_AARCH64_LD64_GOT_LO12_NC 0000000000000000 foo + 0 000000000000004c 0000001400000137 R_AARCH64_ADR_GOT_PAGE 0000000000000000 bar + 0 0000000000000050 0000001400000138 R_AARCH64_LD64_GOT_LO12_NC 0000000000000000 bar + 0编译 main.c 不开启 HWASAN,编译 global.c 时开启 HWASAN,但是关闭 HWASAN 对全局变量相关的内存错误的检测。
$ clang -fno-PIC -fsanitize=hwaddress -mllvm -hwasan-globals=0 -c global.c -o global.hwasan.noglobals.o $ clang -fno-PIC -c main.c -o main.o $ clang -fuse-ld=lld -fsanitize=hwaddress main.pic.o global.hwasan.noglobals.o -o a.out
参考链接
P.S.
我在调试 lld 学习重定位时,在 lld/ELF/Symbols.cpp 中看到如下代码注释,分享出来:
// In the typical case, this is actually very simple and boils
// down to adding together 3 numbers:
// 1. The address of the output section.
// 2. The offset of the input section within the output section.
// 3. The offset within the input section (this addition happens
// inside InputSection::getOffset).
//
// If you understand the data structures involved with this next
// line (and how they get built), then you have a pretty good
// understanding of the linker.
uint64_t va = isec->getVA(offset);